The Tree Swallow (TRES)
is a migratory passerine bird that breeds in North America and winters
in southern U.S., Mexico,
Central America and the Caribbean. They're the species of choice for
many North American ornithologists pursuing songbird research. This blog
entry presents the results of the first four years of a pilot project
involving a TRES population and describes and discusses how these birds
established themselves on a remarkable location. It will also look in
the future of what possibly is one of the most isolated breeding
populations of this species in North America.
Surprisingly, Rausch (1958), who thus far published the only
complete breeding bird inventory for the island, mentions the TRES as a breeder in 1956,
as he observed a few of these birds nesting in the remains of a building. I
would later found out this building was a U.S. Coast Guard station located in the
center of the island, which was only operational for a few years during World War II.
This building got burned down in 1960, probably eliminating the
species from the island as a breeder during the following years.
With
an increasing interest in historical records of the breeding
species of Middleton Island (I've been working on an avifauna for the
island for a while now), I would later find out that during the
following
decades the TRES made irregular appearances as a breeder, with at least one
pair utilizing cavities in a building within an abandoned FAA settlement
in the north end of the island where it got recorded nesting
occasionally during 1976 - 2002. Unfortunately for these birds this
settlement
got removed during the summer of 2005, again leaving them
without a place to nest on the island.
In 2011
I did not visit Middleton due to other obligations, but prior to the
summer I asked
the USGS seabird volunteers to keep their eyes out on the TRES
development. Thankfully they did and by the end of the summer I was
pleased
to receive an overview of the results of their nest box inspections. It
appeared that seven boxes contained at
least some nest material, of which four boxes contained completed nests
on June
10. Three of these nests contained eggs on this day (box 2: five eggs; box
4: five
eggs; box 6: two eggs). During a second inspection on June 16, box 2 and 4
still
contained five eggs, box 6 contained six eggs and box 7 contained a completed
nest but
no eggs. On these dates some nest material was also found in box 1 ('few
straws'), 9 ('few straws') and 12
('cup with no bottom'), but these would not result in clutches, neither
did box 7. No inspections
were made during chick stage, but the boxes were all checked after chick
departure and their contents, as observed by them on August 3, gives good
information about the
TRES productivity for 2011: box 2 contained an empty nest, indicating
that five
chicks had probably fledged from this box. Box 4 contained an unhatched
egg and the comment that three chicks fledged from this box (which
leaves the fate of one egg unclear). Box 6 contained two dead chicks and
fledging for the other four was
assumed.
Based on these data I suspect that in 2011 at least five TRES pairs occupied the boxes, of
which three produced eggs, resulting in a total of 16 eggs, and these birds fledged at least 12 out of 14 chicks.
Unfortunately, no chicks could be banded in 2011. This year would be the first year that an unhatched egg and dead chicks were
found.
The 2012 season: a good start, but a near total failure... - This year the TRES activity got monitored by Mark Baran and Kyle Elliot, who both visited Middleton as part of their seabird research out there. Kyle informed me the first TRES was seen on May 12. The first eggs were laid probably just after Kyle left the island for his mid summer break, but throughout the summer Mark did an excellent job in recording the development in and around the nest boxes and even managed to band the birds this season.
In 2012, five pairs laid eggs during the first two weeks of June. I assume the earliest laying date was June 2, as five eggs were found in box 8 on June 7 (the largest clutch on that date; they lay one egg a day, I believe). On this date box 1 contained one egg; box 6 contained three eggs, box 9 contained four eggs and box 17 also contained four eggs. During the following inspection on June 15 most nests were found to contain completed clutches: box 1: six eggs; box 6: six eggs; box 8: six eggs; box 17: seven eggs (the first seven-egg clutch recorded for this project!). Box 9, however, only contained three eggs and one broken egg. Mark noted that this box had been abandoned by the birds at this time.
During the inspection of June 22 not much changed, but box 1 lost an egg (broken) and went back to five, box 8 contained the first (two) chicks for the season and one egg disappeared form the seven-egg clutch from box 17, which would later be found broken. A little bit of nest material showed up in box 4, but this would not result in a finished nest and was probably not the work of another pair. On this date Mark managed to capture three of the breeding birds from their nest for banding (from boxes 1, 6 and 8). With still four pairs, 21 eggs and two chicks on the list it would not appear to be a bad season.
Unfortunately, during the following chick stage the situation would turn very bad. Box 1 contained four chicks and one egg on June 30, but these chicks were all found dead on July 7 and the remaining egg would not hatch and was later found broken. By June 30, box 6 contained five chicks and an egg. Of these chicks four were still alive by July 3 and these were banded, but all were found dead in their nest by the end of the season and the remaining egg apparently never hatched. In box 8 five chicks were present on June 29, and these were all banded on July 3. During the final inspection on August 11, however, two of these chicks were found dead, resulting in three fledged chicks that left their box during the second half of July. On June 27, box 17 was found to contain five chicks and one egg (which would later be found broken in the nest). Of these chicks only three were still alive on July 7 and these were banded, but only two managed to fledge during the second half of July; the three dead chicks were removed from the nest box during the final and cleanup round on August 11. Based on this information, in 2012, five pairs occupied the nest boxes and these laid a record number of 29 eggs, but these resulted in the fledging of only five chicks. Besides these breeding pairs, there may have been one or more lonely males
occupying nest boxes for a while, but without success.
 |
| Contents of Box 17 on July 7, 2012 (photo: Mark Baran) |
 |
| Contents of box 17 on July 7, 2012: three live chicks and two dead; only two would fledge (photo: Mark Baran) |
Results - an overview (2009 - 2012):
Discussion
The first four years of this project have shown that, as throughout most of the
North American continent, on Middleton Island the TRES can easily be
persuaded to nest in nest boxes. Throughout Middleton’s recorded history, the TRES has shown to have a close relationship with human presence on the
island, as the species appears to be totally dependent on human constructions
for its nest sites. Without people’s activities, there most likely would not be
any TRES nesting there. So, why would I put effort in establishing a TRES population on Middleton if the species would not nest there
without the presence of man? Well, I could come up with several reasons:
- History has shown that there are TRES that apparently want to nest on Middleton. I'd like to help them doing so.
- As long as there is human activity on the island, I believe it’s good to
do something positive for the bird communities by increasing the island’s breeding
bird diversity. I expect the presence of a TRES breeding population to (thus far) be of
a minimal influence on the other bird species present out there.
- Personally, after my first close encounter with this species in 2009, I
believe they’re one of the most enjoyable species around. I was very pleased to
see their playful flight and hear their friendly chattering calls above
Middleton’s grassy plains, which otherwise can be a bit boring. I hope other
people enjoy this too.
- Due to the island’s isolated location, size and the presence of an onsite
weather station, Middleton Island would theoretically be a perfect place to study a TRES
population. I am hoping that by having a descent number of these birds nesting
there annually, monitoring these could make an interesting contribution
to scientific research in general, in order to find out more about the island’s bird
populations, as well learning more about the TRES itself.
- And finally, I don’t like bugs very much. The TRES eats loads of bugs,
so as far as I’m concerned they’re welcome there.
But what about the TRES itself? Is life good for a TRES on the remote Middleton
Island? At first sight, it seems that food appears to be widely
available to them and with the absence of ground predators, only an irregular
presence of almost only a single aerial predator species during the breeding
season (the Peregrine Falcon, Van Nus, personal records) and the absence of
competing species around their nest sites, a TRES can certainly have a good
time out there. However, although the first two
years of this study have shown that these birds can indeed have great breeding success,
hatching a good number of eggs and fledging an equally good number of young, the
results of this study’s third and especially its fourth year show that this is not always the
case.
By now, the main cause of breeding failure seems
obvious: with the exception of a some rainy periods during my stays on the island
in 2009 and 2010, I suspect that continuing periods of bad weather that later
field crews had to endure determined the relatively poor breeding results of
the 2011 and 2012 seasons. After the almost disastrous 2012 season, both Mark
Baran and Kyle Elliot informed me that bad weather conditions
out there during the chick stage most likely were the cause of the poor breeding results
in that year (and I can’t recall seeing a single sunny day when checking the
FAA weather camera regularly throughout the 2012 summer). It seems obvious that eventually bad weather periods limited the foraging
opportunities for the adult birds, resulting in starvation of many of the
chicks. The relative large number of eggs that did not hatch in 2012 may also have been a result of the poor feeding conditions during an earlier stage of the breeding cycle. In 2012 the earliest egg laying date (June 2) was 7 days later than in 2010 (May 26), indicating that conditions were probably not very good at the start of the season. This is all not unique and apears to occur regularly among TRES populations elsewhere, i.e. Kyle informed me he noticed the same thing happening with the TRES nesting at the Long Point Bird Observatory in Canada and Alexandra Rose informed me she had a very bad 2012 season as well at Long Lake (almost exactly 100 miles northeast of Middleton), with massive nestling mortality. Unfortunately, only
current weather data from the island appears to be available online and I can’t
find a climate summery for any of these four summers anywhere, which would have been nice just to show you what the Middleton birds had to deal with during the first four years of this project.
But has, thus far, life been really so bad for them? Throughout the first four years of this
study, the number of pairs laying eggs appeared to have gradually increased. Their eventual
success on Middleton Island will probably depend on the overall climate
conditions in summer. We can only hope for these birds that during future summers the
climatic conditions will be better than they were in 2012, but they certainly will not always be.
Even with some very good breeding results and over the years still a good number of
young fledging, compared to mainland colonies, the population increase that occurred during the first four
years seems to be somewhat slow (I would love to compare this with data from the establishment years of other colonies, but I haven't managed to find this). Though the reason for the slow population growth has not been
studied, I speculate that thus far the following scenario may have taken place:
Regardless of the bird’s breeding results in any previous year, the number
of birds that nest on the island largely depended on a number of breeding birds
from a previous year that managed to return to the island + an additional small number of ‘floaters’
(young, inexperienced birds) that shows up there in spring, usually late May. I do not know much about the annual survival of
the breeding birds, but based on the records of the number of TRES
that pass by the island in spring (before the establishment of this breeding
population) I think that these could well account for the additional number of
pairs that were found with each new year. I do not have many records of TRES observations in spring, simply because they were rarely seen, but because of the number of birds observed on
these occasions (0-8, mostly 2-4, Van Nus, personal data), as well as the timing of the majority of these birds (last week of May) in
relation to the initiation of nesting of the breeding pairs, I suspect that Middleton does not make part of the
normal flyway for this species in spring and TRES would only show up there irregularly. With a number of birds arriving relatively early during the later three
years of this project (May 10, May 12), I suspect that at least some of the
experienced breeding birds are aware of their destination and these were deliberately
heading to a Middleton Island nest box.
Whatever happens to the young that are born on the Middleton Island, thus far remains a
mystery. As there appear to be no recorded
observations for this species on Middleton in the fall, I suspect that Tree
Swallows do not migrate above the Gulf of Alaska easily. I suspect it will not be easy for them to make their first fall
migration, as they may have to cross several hundreds of kilometers of ocean.
This makes me very uncertain about their survival, as well as their return rate
to the island during a following year.
With the re-establishment of the TRES on Middleton, however, I am suspecting
that with a number of these birds flying around there in spring, this could be a
great attraction for floaters to the nest sites that are offered on the
island, which otherwise may have been overlooked by these birds. Singing
males will attract females, but possibly also other males. But again, these are
all speculations, and not the result of a scientific study. The only way to get
more insight in the way this remote population works is by continuing the TRES banding activities out there.
At this point the only thing I’m pretty sure about is that slowly more and more
Tree Swallows are finding their way to Middleton Island and there are currently
more pairs nesting out there than ever before.
 |
The spring and fall migration routes that are used by Middleton's Tree Swallows remain unknown.
Do they take the shortest way? Do they fly hundreds of kilometers over the North Pacific Ocean?
Do the chicks all migrate south and find a watery grave? |
|
|
The future of this project and priorities
for further research
How many TRES pairs Middleton Island eventually can host remains unknown. The number of Bank Swallows nesting there (65
- 112 pairs (2005 - 2010)) could indicate that swallows may be able to hold large populations out there,
but as this is a different species, it will be hard to make a comparison. In fact, in 2009 the first two TRES pairs seemed to be doing very well, whereas during the same season the 65 pairs of Bank Swallows remained largely unproductive... (Van Nus, personal records)
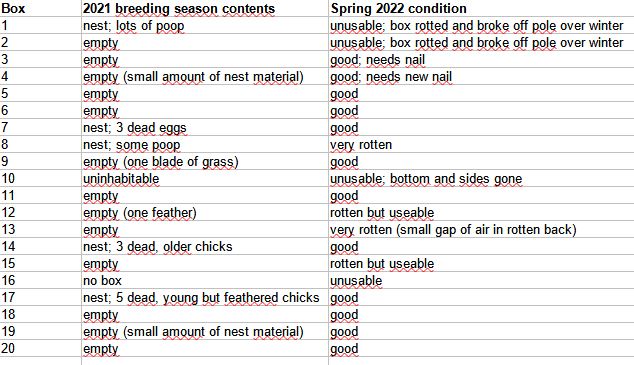
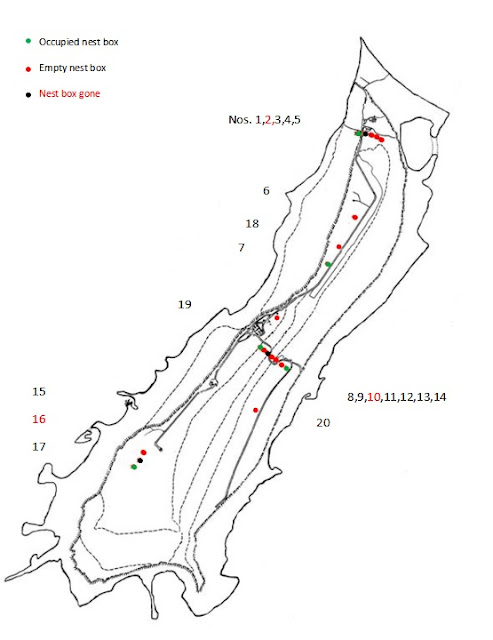
With
17 nest boxes still present and only a maximum of about seven boxes occupied (including
the non-breeding and lonely males) it seems that no new boxes need to be added yet.
The people who kept their eyes on the TRES during the previous year informed
me that the boxes are still in good shape and do not need to be
replaced yet. As a side note: as mentioned before, the current boxes have been
built by using the sizes recommended by the Golondrinas project. However,
except for one. Throughout the first four years of the Middleton Island project,
the swallows have occupied and laid eggs in seven of the 17 boxes (1 x
in box 1; 2 x in box 2; 1 x in box 4; 4 x in box 6; 2 x in box 8; 1 x in box 9
and 1 x in box 17). According to this information, nest box 6 (shown on a photo
above) has been the most popular box thus far, being used in every summer and producing more fledglings than any other box (16 fledglings in total). Box 6 was made about an inch less deep and the internal
sizes are about half an inch bigger than the others. I suspect the birds prefer
the dimensions of this box more than the others, which seems obvious for a secondary cavity nester, but it could all just have been a coincidence. In any way, these alternative sizes may be recommendable when adding an additional number of nest boxes in the future.
The presence of the onsite weather station is a bonus for this project. However, it would be very useful when the gathered climatic data would actually be stored somewhere and when this would become available online (at least I'd never managed to find this).
Above all, it has become important that, in order to
continue to generate good quality data, in future years a standardized method
for monitoring the TRES population development on Middleton Island, in and
outside of their nest boxes, gets applied. In order to get to know more about
the structure of this population and the project’s future perspectives, during
the upcoming years banding of the chicks and (re)capturing and banding of the
adult breeding birds should be considered a priority. Middleton may be the
ideal study site for a number of reasons, but this has yet to be proven.
Short video footage of the swallows of Middleton Island in 2010.
Acknowledgements
I thank all the people that were involved and that helped me out with the TRES-project thus far. Thank you for either helping building and placing some boxes or helping me conducting nest box checks or ringing chicks of the few pairs in 2009 or 2010 (Veronique Frochot, Christophe de Franceschi, Lauren Bessey, Joel White, Paul Solis and Kyle Elliot). During 2011, Lena Agdere, Mike Johns, Sharon van den Eertwegh, Chris, Lucy (sorry, couldn't find your last names) and Thomas Merkling all did a great job monitoring the boxes. In 2012 Mark Baran did a great job too, monitoring and banding the swallows during his rainy stay and he got thoroughly instructed by Kyle Elliot. I'd like to thank Scott Hatch (USGS) for letting me use the necessary power tools to construct 17 nest boxes from scratch and also for supplying the TRES bands. I thank Chris Gates for supplying me with the required information about starting up a project involving this fascinating species.
Literature
Rausch R. 1958. The occurrence and distribution of birds on Middleton Island, Alaska. The Condor 60: 227-241.